Bitcoin and Blockchain Technology
- The technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is also gaining traction in the business world due to its ability to create a secure network that can easily track a large amount of data.
- In this Investment Insights, we discuss what blockchain technology is and the technology’s business applications.
What is Bitcoin and Blockchain Technology?
Bitcoin is currently the largest type of cryptocurrency in terms of market cap and trading volume.1 Bitcoin along with other cryptocurrencies are traded through online exchanges, including the U.S.-based exchanges, Coinbase and Gemini. In comparison, fiat currencies are traded through the foreign exchange market, which is the largest financial market in the world and includes numerous market participants (e.g., commercial banks, central banks, retail traders, and investment firms). Unlike fiat currencies, which are issued by central banks, cryptocurrencies are generated through a process called mining and rely on peer-to-peer technology in the form of blockchain technology. Each individual that successfully adds a new block to the chain is rewarded with Bitcoins once the members of the blockchain network collectively validate the transaction. No central banks or governments oversee these transactions.
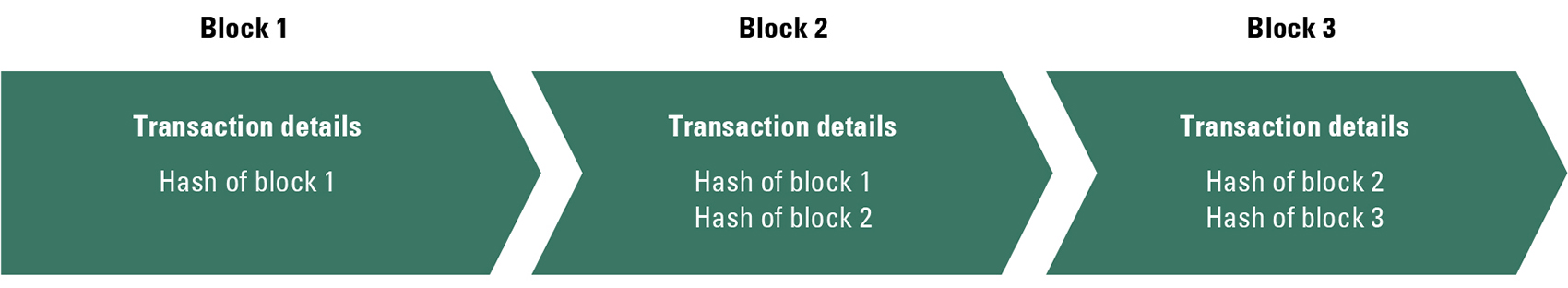
In essence, blockchain technology is a sequential transaction database that is consensually shared and synchronized across a network. The first block is the initial transaction. Once a transaction occurs, a new block is added that contains a unique code linked to the prior transaction. New blocks are added through the mining process. For instance, if Michael has $100, the first block would indicate that he has $100. If Michael then gives $15 to Claire and $20 to Steven, the next block would list these transactions and contain the code that would tell all members of the blockchain that Michael started with $100 and two subsequent transactions with Claire and Steven; the members of the network must validate the transactions before a new block can be added.
Each block is encrypted with a unique code, called a hash, and includes the common transaction details and unique signatures of the parties involved in the transaction as well as a timestamp (Exhibit 1). Mining occurs when the members of the blockchain solve for the unique hash using software specifically designed for this. All new blocks are linked to older blocks in chronological order, so all members of the network can see the transaction history and must approve of each new block added to the chain.
If a member of the blockchain makes a change to one of the blocks that has already been completed, all the subsequent blocks need to be changed. This is because the hash has changed, and all the following transactions are based on the now old hash. The person who changed the hash must then recode all the invalid transactions via mining before any new blocks can be added to the network. This takes a tremendous amount of time and more computing power than most individuals have access to. Additionally, all the members would know that a change has been made to one of the blocks. This provides a sense of security to all content within the network and is the comparative advantage of the technology. It is this element that makes blockchain appealing to the business world.
Additionally, blockchain technology can be split into two forms: public and private. Public blockchain simply means that anyone who takes part in the transaction can also read and write within the entire database. Cryptocurrencies are examples of public ledger and are ideal for their functionality because the individual members do not know each other.
Private blockchains function in the same way as public ones, but each member must be approved via pre-validated market IDs in order to participate. Many members of the business world are finding applications for private blockchains due to their needs for transaction privacy.
Applications for Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has many applications beyond cryptocurrencies. Many businesses are taking note of its value and partnering with technology companies to implement solutions using blockchain. Below we highlight some examples.
- • In the shipping industry, hundreds of transactions take place to transport one container. For instance, Maersk stated that one shipping container going from East Africa to Europe requires paperwork involving 30 different people and totals 200 or more interactions. Maersk has partnered with IBM to improve this process using blockchain technology that allows all participants in the supply chain to track the shipment from start to finish. The goal is to reduce the amount of paperwork and enable customs officials and clients to track where the products are at all times.
- Walmart partnered with IBM to test the use of blockchain to track its produce. More specifically, like many retailers, Walmart was finding it difficult to notify its consumers of product recalls or when a consumer becomes ill from a product. The hope is that blockchain will solve this issue by creating a centralized database to record the entire transaction history of a product including its suppliers, how and where the food was grown, and who inspected it. This data would be retrievable through the consumer’s receipt, enabling Walmart to strategically remove only the contaminated items and quickly identify the sources of foodborne outbreaks, like E. coli.
- Blockchain is also being explored as an option to significantly cut down on cash settlement times. The U.S. cash equities market is the largest and most active market in the world, totaling an average of 7 billion shares with a notional value of $277 billion traded per day as of 2015. Exchanges, like NASDAQ and NYSE, broker-dealers, custody banks, and Depository Trust Company (DTC) are all involved in the process.
- The cash settlement process takes around two days to be completed, and each of the parties involved in the process has their own system for processing the transaction that can result in disagreements on trade details. Blockchain technology can improve the cash settlement process by reducing trade errors, since all records require verification among all nodes in the network. The reduction in trade errors would also reduce the headcount and number of platforms and systems in back and middle offices. Lastly, a reduction in the settlement time would improve the efficiency of the capital market systems and reduce some market risk.
- Along with IBM, Microsoft has positioned itself as a top player in blockchain technology. Microsoft’s Azure developed Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) to provide a platform for businesses to utilize blockchain technology via a cloud computing platform. Ethereum and Hyperledger, which are both public blockchains, are supported by Microsoft Azure. In essence, Microsoft’s goal is to offer companies an open platform supporting different blockchain developers to allow them to select the best technologies for their business application.
- Microsoft is also a member of the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance. This consortium’s goal is to develop more business-oriented solutions using Ethereum’s open-source blockchain technology and includes tech giants, such as Intel and Microsoft; large financial firms, such as J.P. Morgan, Credit Suisse, UBS, and BNY Mellon; and start-up firms.
Conclusion
While we recognize the value of cryptocurrencies, we do not invest in them. At this time, there are too many outsized risks and other investment opportunities with more attractive risk-adjusted return prospects. The blockchain technology behind these currencies, however, is potentially transformative and disruptive to many industries. We do have indirect exposure to blockchain technology in our equity mandates through investments in companies that are utilizing or plan to utilize the technology to improve their business practices.
Past performance is no guarantee of future results. This material is provided for your general information. It does not take into account the particular investment objectives, financial situations, or needs of individual clients. This material has been prepared based on information that Bessemer Trust believes to be reliable, but Bessemer makes no representation or warranty with respect to the accuracy or completeness of such information. Views expressed herein are current only as of the date indicated, and are subject to change without notice. Forecasts may not be realized due to a variety of factors, including changes in economic growth, corporate profitability, geopolitical conditions, and inflation. The mention of a particular security is not intended to represent a stock-specific or other investment recommendation, and our view may change at any time. Digital currencies are highly volatile and not backed by any central bank or government. Digital currencies lack many of the regulations and consumer protections that legal-tender currencies and regulated securities have. Due to the high level of risk, cryptocurrency should be viewed as a purely speculative instrument.